
Bulk Google Index Checker
First of all let us explain what is Google Indexing and how to Bulk Google Index Checker .
Google indexing refers to the process by which Google updates its library of Internet web pages. An index, when we talk in terms of the online landscape, is like a gigantic catalogue of every web page that Google is aware of. Simply put, Google indexing is how Google gathers pages to show for any query in the search results.
Understanding the Internet’s Library System – How Google Indexing Works:
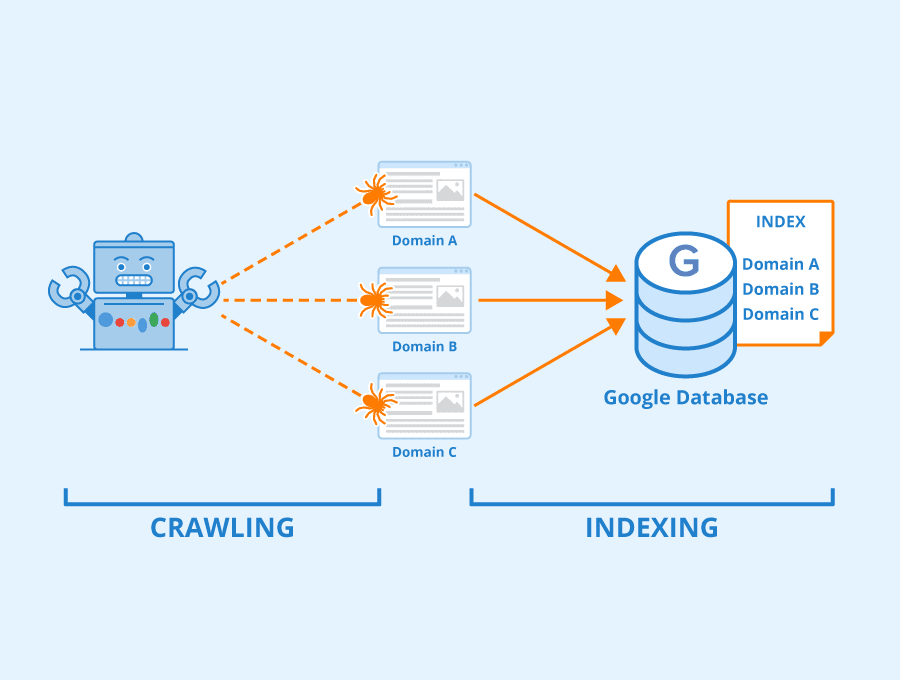
The indexing process begins when Google’s bots, also known as crawlers or spiders, roam around the web, visiting pages and collecting information. Their primary job is to track the Internet’s billions of pages, indexing new sites, updates to existing sites, and dead links. The ‘Googlebot‘ discovers new and updated pages to include in Google’s index via a method called crawling.
When the Googlebot visits a site, it collects information about its content, where it’s located, and much more. This data is then compiled into an enormous library — the Google Index. This index is then matched against search queries to provide users with the most relevant results based on their search terms. It implies that whenever a user enters a prompt in the Google search bar, Google doesn’t browse the whole web but simply searches its index.
Google’s Web Crawlers and How They Aid in Indexing:
Google’s web crawling software, Googlebot, scans web pages across the internet and adds them to the Google index. Keeping up with the constantly-evolving Internet, Googlebot must make frequent return visits to ensure the indexed websites remain up-to-date in Google’s index.
The Googlebot begins its task by fetching a few web pages, and then follows the links on those pages, much like the spreading branches of a tree. As the Googlebot discovers new sites or adds new information to the index, these sites, or changes, are then ranked in relevance to a search.
How Google Decides What to Index?
Google’s indexing systems note many aspects of pages as it crawls and indexes them. Several key factors determine whether or not a page is indexed by Google:
1. The page’s Meta tags: The Googlebot pays particular attention to the title tag and the meta description tag, which provide basic information about the page.
2. File Types: Google can index most types of pages and files, including PDFs, Excel spreadsheets, and PowerPoint presentations.
3. Page Content: Google indexes the visible content on a page, along with the underlying code.
4. Quality of content: Pages that contain high-quality, original content are more likely to be indexed than pages with duplicate content or content of little value.
5. Page design: Pages that are well-organized and easy for users to navigate are more likely to be indexed.

Importance of Google Indexing:
Understanding Google indexing is integral for webmasters and SEO professionals as this influences a website’s visibility in the search engine result pages (SERPs). Subsequently, it impacts the website’s organic traffic flow and overall online presence.
How to Enhance Your Google Indexing?
Optimizing a website for Google indexing begins with the overall quality and structure of the site. Here are some strategies to improve your site’s Google indexing:
1. Sitemaps: A well-structured sitemap allows Google’s bots to navigate the site more efficiently to index.
2. Robots.txt Files: These files indicate which pages on your site you do not want Googlebot to crawl.
3. Serving High-Quality Content: Websites with original, useful content will quickly rise in Google’s index.
4. Fast Loading Speed: A fast-loading site not only enhances user experience but also increases the likelihood of being indexed fast and frequently by Googlebot.
5. Mobile optimization: Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly will give it an edge since Google now uses mobile-first indexing.
6. Register Website with Google Search Console: It allows you to directly ping Google to crawl and index your website.
With an evolving search landscape, optimizing for Google indexing has become more complex yet crucial. It remains an imperative part of Search Engine Optimization strategy, extending a significant influence on the visibility of a website. However, with a firm understanding of the Google Algorithm and effective SEO practices, one can efficiently enhance Google indexing. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of Google indexing – its core function, its importance, and how it works to ensure that every web page on the internet is accounted for.
Ensuring your website is indexed on Google is crucial for online visibility. Traditionally, users have relied on Google’s own website to check individual URLs for indexing. While this method is straightforward, it poses limitations and can be time-consuming, especially for those managing multiple websites. This article explores the traditional method of checking URL indexing on Google, its limitations, and presents alternative tools that offer bulk indexing checks, categorized into free and paid options.
How to check your links if they are indexed by google ?
Traditional Method: Google Search Console
The traditional approach involves using Google Search Console to check if a specific URL is indexed. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Access Google Search Console:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select the property (website) you want to check.
- Navigate to the Index Coverage Report:
- Go to the “Index” section on the left-hand side.
- Click on “Coverage.”
- Enter URL for Inspection:
- In the “Coverage” report, enter the specific URL you want to check.
- Click on “Request Indexing” if the URL is not indexed.
Limitations of the Traditional Method:
- One-by-One Checking:
- The traditional method allows checking only one URL at a time, making it time-consuming for websites with numerous pages.
- Limited Insights:
- Google Search Console provides basic information but lacks the comprehensive data some webmasters may require.
Alternative Tools for Bulk Google Index Checker:
Free Options:
- Duplichecker:
- Allows checking up to 10 links for free.
- Indexchecking:
- Supports checking up to 25 links at once.
- Rankwatch:
- Provides free bulk checking for up to 25 links.
- SmallSEOTools:
- Offers free bulk checking for up to 5 links.
- SearchEngineReports:
- Allows users to check up to 5 links in bulk for free.
- ShortURL.live:
- Supports checking up to 30 links for free.
Paid Options:
- Indexcheckr:
- Utilizes a credit system, with 1 credit per link checked.
- Linkbox:
- Operates on a credit basis, where 1 credit equals 1 link checked.
- IndexedAPI:
- Follows a credit system, with 1 credit required per link checked.
Differentiating Factors between Free and Paid Options for Bulk Google Index Checker:
- Limitations on Free Services:
- Free services typically have a link limit, ranging from 5 to 30 links depending on the platform.
- No Link Limits for Paid Services:
- Paid services offer the advantage of checking an unlimited number of links without any restrictions.
While the traditional method provided by Google Search Console remains a reliable option, the limitations in terms of one-by-one checking make it less practical for websites with extensive content. Utilizing free or paid bulk URL indexing tools can streamline the process and offer a more efficient way to monitor and manage the indexing status of multiple URLs simultaneously. The choice between free and paid options ultimately depends on the specific needs and scale of the website.
The frequency with which you need to check the indexing status of your URLs depends on various factors, including the size of your website, how often you update or add new content, and your overall SEO strategy. Here are some considerations:
Regular Monitoring:
- Content Updates:
- If you frequently update or add new content to your website, it’s advisable to check indexing regularly. This ensures that search engines promptly discover and index your latest content.
- Site Changes:
- If you make significant changes to your site structure, such as URL restructuring or redesigns, it’s essential to monitor indexing to identify and address any issues promptly.
- Algorithm Updates:
- Search engine algorithms can change, affecting how content is indexed. Regular monitoring allows you to adapt to these changes and maintain optimal visibility.
- Monitoring for Issues:
- Regular checks help identify indexing issues, such as crawl errors, that may affect your website’s performance in search results.
One-Time Checks:
- Static Content:
- For static websites with infrequent updates, a one-time check may be sufficient. However, it’s still a good practice to periodically confirm the indexing status.
- Established Websites:
- If your website has been around for a while, and you haven’t made significant changes, less frequent checks may be acceptable. However, occasional monitoring is still recommended.
Best Practices:
- Sitemap Submission:
- Submitting an updated XML sitemap to search engines whenever you make changes to your site is a good practice. This can expedite the indexing process.
- Google Search Console Alerts:
- Set up alerts in Google Search Console to receive notifications of potential indexing issues. This way, you can address problems as soon as they arise.
- SEO Strategy:
- Consider your overall SEO strategy. If SEO is a crucial part of your online presence, regular monitoring is vital to ensure your site performs well in search results.
In summary, the frequency of index checking depends on the dynamic nature of your website. For active websites with frequent updates, regular monitoring is advisable, while one-time checks may suffice for static or less frequently updated sites. Monitoring tools and services can help streamline this process and provide valuable insights into the indexing status of your URLs.

